A Decade Of Stability: Unraveling The Significance Of The Ten-Year Treasury Yield
Introduction
Over the past ten years, the Ten-Year Treasury Yield has played a pivotal role in shaping global financial markets, acting as a reliable benchmark for interest rates and influencing various economic sectors. As we delve into its significance, behavior, and impact, this article explores how this crucial bond yield has affected investors, governments, businesses, and the broader economy. Throughout the past decade, the Ten-Year Treasury Yield has undergone significant fluctuations, reflecting shifts in market sentiment, economic conditions, and monetary policy. By understanding its historical context and examining its implications, we can better grasp its importance in modern financial landscapes.
The Ten-Year Treasury Yield: An Overview
The Ten-Year Treasury Yield represents the yield on the U.S. government’s ten-year debt obligation. It serves as an essential benchmark for investors and economists worldwide, as it reflects the interest rate that the government must pay to borrow money for a ten-year period. This rate is heavily influenced by factors such as inflation expectations, monetary policy decisions, and global economic conditions.
The Role Of The Ten-Year Treasury Yield In Financial Markets
The Ten-Year Treasury Yield is instrumental in guiding financial markets. Its fluctuations impact a wide range of financial instruments, including mortgage rates, corporate bonds, and other long-term interest rates. Investors often view the yield as a “risk-free” rate of return, which influences their investment decisions across various asset classes.
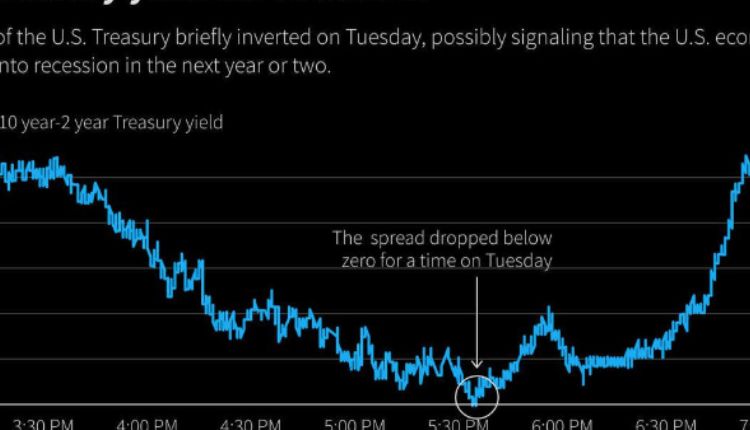
Economic Indicators And The Ten-Year Treasury Yield
The Ten-Year Treasury Yield is closely observed by economists and policymakers as it can act as a leading economic indicator. Changes in the yield curve, which plots the yields of various maturities, can signal shifts in economic growth expectations. An inverted yield curve, where short-term yields are higher than long-term yields, has historically preceded economic downturns.
Factors Influencing The Ten-Year Treasury Yield
Numerous factors impact the fluctuations of the Ten-Year Treasury Yield. Federal Reserve policies, inflation expectations, geopolitical events, and global economic conditions all play significant roles in determining its trajectory. Unraveling the interplay between these elements is essential in understanding how the yield evolves over time.
The Ten-Year Treasury Yield And Investor Behavior
The Ten-Year Treasury Yield heavily influences investor sentiment and behavior. In times of economic uncertainty, investors often flock to safer assets like Treasury bonds, driving their prices higher and yields lower. Conversely, during periods of economic growth and optimism, investors may shift towards riskier assets, resulting in increased yields.
Government Debt And Fiscal Policy Implications
The Ten-Year Treasury Yield has profound implications for governments and their fiscal policies. As the benchmark for long-term borrowing costs, fluctuations in the yield can impact government debt sustainability. Higher yields can increase interest payments, potentially leading to budgetary challenges.
- Impact on Corporate Borrowing and Business Decisions
The Ten-Year Treasury Yield also has an important bearing on corporate borrowing costs. Since many corporate loans and bonds are priced relative to Treasury yields, fluctuations can affect the overall cost of capital for businesses. This, in turn, influences investment decisions and expansion plans.
Conclusion
Over the last ten years, the Ten-Year Treasury Yield has proven its significance as a vital economic indicator and a guiding force for financial markets worldwide. Its movements are driven by a complex interplay of factors, ranging from monetary policy decisions to global economic conditions. Investors, governments, and businesses closely monitor its fluctuations as they make critical financial decisions. Understanding the Ten-Year Treasury Yield’s impact on various sectors of the economy can help stakeholders better navigate the ever-changing financial landscape.
FAQs:
Q1: How does the Ten-Year Treasury Yield affect mortgage rates? A1: The Ten-Year Treasury Yield serves as a benchmark for long-term interest rates, including mortgage rates. When the yield rises, mortgage rates tend to follow suit, making borrowing more expensive for homebuyers. Conversely, when the yield falls, mortgage rates often decrease, making homeownership more affordable.
Q2: How does the Ten-Year Treasury Yield relate to inflation? A2: The Ten-Year Treasury Yield is influenced by inflation expectations. If investors anticipate higher inflation in the future, they may demand higher yields on Treasury bonds to compensate for the eroding purchasing power of their fixed interest payments. Conversely, lower inflation expectations can lead to lower yields as investors seek safer assets.







